Purchase order processing requires distributing allocating, a critical aspect of the procurement process that ensures the seamless flow of goods and services within an organization. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of distribution and allocation, providing a clear understanding of their significance and the best practices involved.
From defining the concepts of distribution and allocation to exploring the various methods and procedures used, this Artikel covers the entire spectrum of purchase order processing. By delving into real-world examples, case studies, and technology solutions, this guide empowers readers with the knowledge and strategies to optimize their purchase order processing systems.
Purchase Order Process Overview
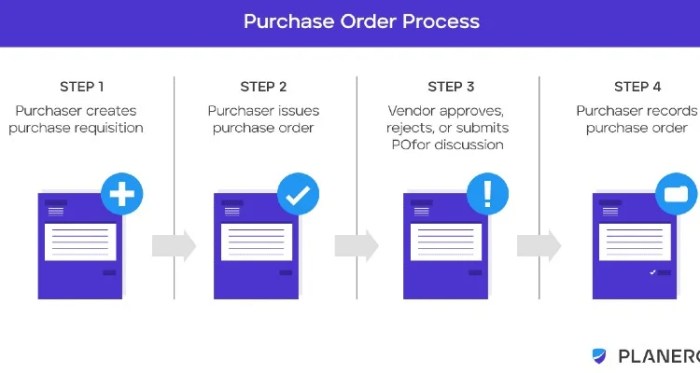
Purchase order processing encompasses a series of steps that ensure the efficient acquisition of goods and services. It involves the collaboration of various departments, each with specific roles and responsibilities.
The typical steps in purchase order processing include:
- Initiation of purchase request
- Vendor selection and price negotiation
- Issuance of purchase order
- Receipt of goods or services
- Invoice verification and payment
The flowchart below illustrates the typical purchase order processing flow:
[Flowchart Purchase Order Processing]
Distribution and Allocation
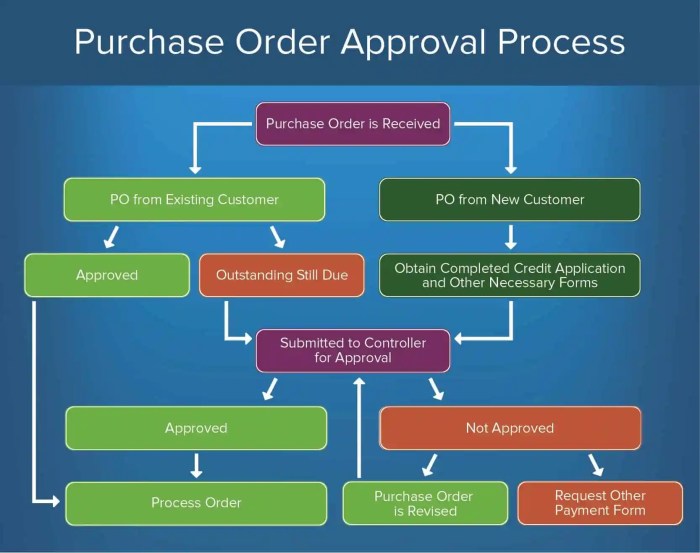
Distribution and allocation are crucial aspects of purchase order processing, ensuring the appropriate distribution of goods and services and the assignment of costs and expenses.
Distributionrefers to the physical delivery of goods or services to designated locations or individuals. Allocationinvolves assigning costs and expenses to specific departments, projects, or cost centers.
Factors influencing distribution and allocation decisions include:
- Availability of resources
- Business requirements
- Cost-effectiveness
Distribution Methods
Various distribution methods are employed in purchase order processing, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Direct delivery:Goods are delivered directly to the end user or designated location.
- Cross-docking:Goods are unloaded from incoming vehicles and directly loaded onto outgoing vehicles without being stored.
- Warehousing:Goods are stored in a warehouse and distributed as needed.
- Dropshipping:The supplier handles the storage and delivery of goods directly to the customer.
Allocation Procedures, Purchase order processing requires distributing allocating
Allocation procedures are used to assign costs and expenses to specific cost objects. Common allocation procedures include:
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Activity-based costing (ABC) | Costs are allocated based on the activities performed. |
| Percentage of sales | Costs are allocated based on the percentage of sales generated by each department or project. |
| Equal allocation | Costs are allocated equally among all cost objects. |
Challenges and Best Practices
Purchase order processing faces several challenges, particularly in distribution and allocation:
- Ensuring timely delivery of goods and services
- Optimizing distribution routes to minimize costs
- Accurately allocating costs and expenses
Best practices for overcoming these challenges include:
- Implementing efficient inventory management systems
- Utilizing technology to automate distribution and allocation processes
- Establishing clear policies and procedures for cost allocation
Technology and Automation

Technology plays a significant role in automating purchase order processing, including distribution and allocation. Software solutions such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can streamline these processes by:
- Automating the creation and issuance of purchase orders
- Tracking the status of goods and services throughout the distribution process
- Allocating costs and expenses based on predefined rules
Commonly Asked Questions: Purchase Order Processing Requires Distributing Allocating
What is the difference between distribution and allocation in purchase order processing?
Distribution refers to the physical movement of goods or services from the supplier to the requesting department, while allocation involves assigning costs and expenses to specific departments or projects.
What factors influence distribution and allocation decisions?
Factors such as product availability, lead times, storage capacity, and departmental budgets play a role in determining distribution and allocation strategies.
What are some common challenges in purchase order processing related to distribution and allocation?
Challenges include inaccurate inventory data, inefficient communication between departments, and lack of automation, which can lead to delays, errors, and increased costs.